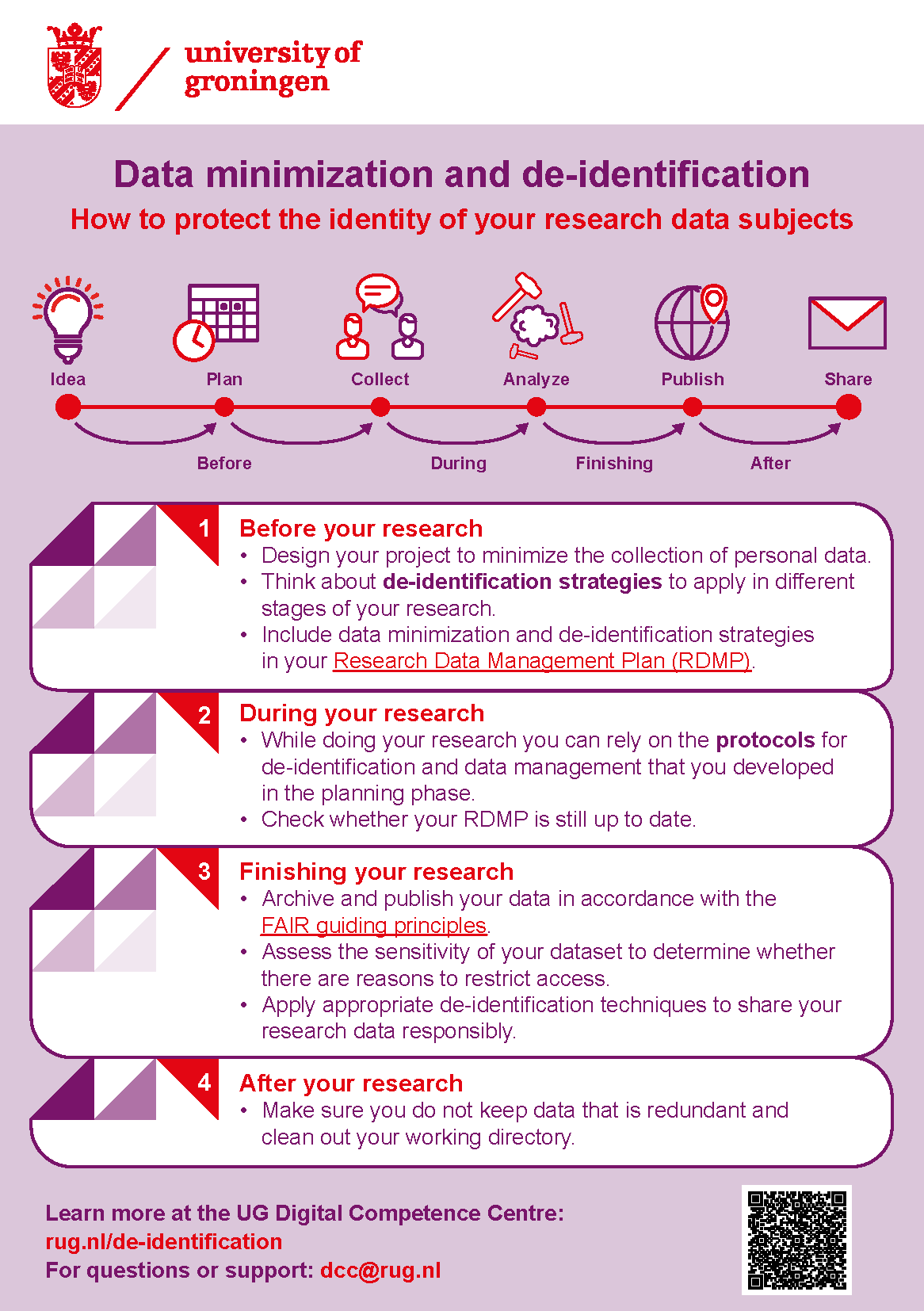
Data minimization & de-identification
As a researcher, you are responsible for protecting the privacy of your data subjects. For this reason, the principle of data minimization (GDPR art. 5 (1c)) should be one of the leading in the design of your research project. This means that you only collect personal data that is necessary for your research purposes, and de-identify your dataset once personal data is no longer needed to prevent re-identification of your data subjects.
Implementing these safeguards is especially important when you collect sensitive personal data, share data with collaborators or make data available for reuse or verification purposes.
In our guide (PDF) you will learn about:
-
Essential concepts for data minimization
-
How to design your research to limit the collection of personal data
-
Various de-identification techniques
Essential concepts:
Personal data (direct and indirect identifiers)
Personal data
“Personal data is any information that relates to an identified or identifiable living individual. Different pieces of information, which, collected together, can lead to the identification of a particular person, also constitute personal data.” (European Commission).
Direct identifiers
Direct identifiers are data that make it easy to identify an individual, such as name, e-mail address, phone number, home address or IP address.
Indirect identifiers
Indirect identifiers (or: quasi identifiers) are data that do not directly identify an individual, but could, in combination with other identifiers, be unique to an individual and can therefore lead to identification. For example: Women from Groningen who drive a McLaren car. Combined, the underlined identifiers could possibly single out an individual and are, therefore, examples of indirect identifiers.
Examples of indirect identifiers are:
-
Demographics (date of birth, gender, job occupation, etc.)
-
Social media photos
-
Location
-
Any other background information about a specific person.
Granularity
Granularity
Data granularity refers to the level of detail in a data structure or variable. (C3 AI). The higher the granularity in a dataset, the higher the possibility of re- identification.
Data minimization
Data minimization
Data minimization is one of the data protection principles that form the basis of the GDPR. It states that the processing of personal data should be “adequate, relevant and limited to what is necessary in relation to the purposes for which they are processed” (GDPR art. 5 (1c)); Data minimization does not mean that you cannot collect personal data at all. If you can explain why you need these data for the current or specific future purposes you are allowed to collect these data.
De-identification (pseudonymization, anonymization)
De-identification
De-identification is the masking, manipulation or removal of personal data with the aim to make individuals in a dataset less easy to identify.
Pseudonymisation
Pseudonymization is a de-identification procedure during which personally identifiable information is replaced by an unique alias or code (pseudonym). In general, the names and/or contact details of data subjects are stored with this pseudonym in a so-called keyfile. The keyfile enables the re-identification of individuals in the dataset. Keyfiles are stored separately from the rest of the data and access should be restricted. In contrast to an anonymized dataset, a pseudonymized dataset in principle still allows for the re-identification of data subjects.
Anonymization
Anonymization is a de-identification procedure during which “personal data is altered in such a way that a data subject can no longer be identified directly or indirectly, either by the data controller alone or in collaboration with any other party." (ISO 25237:2017 Health informatics -- Pseudonymization. ISO. 2017. p. 7.). In contrast to a pseudonymized dataset, an anonymized dataset does not allow for the re-identification of data subjects and is therefore no longer considered personal data.