Nature news article on nano machines features Ben Feringa
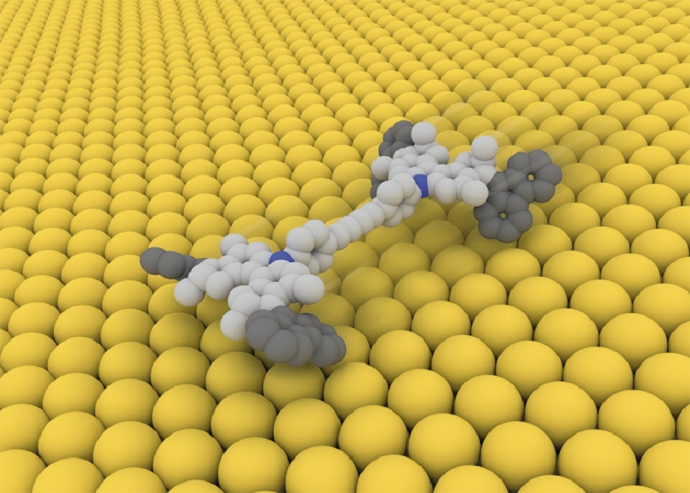
University of Groningen professor Ben Feringa, the organic chemist who made the world’s first light driven molecular motor and a four wheel drive molecular car, is featured in an article on molecular machines published by Nature.
The article describes how the field of ‘the tiniest Lego’ has matured over the last two decades. Many nano machines now exist, giving scientists a well filled toolbox of parts to build with. And although applications are still few, nano switches (in which Feringa also plays a role ) could be used in memory storage, as sensors or as activators of a pharmaceutical compound.
The fact that in June, one of the influential US Gordon conferences focused for the first time on molecular machines and their potential applications is a clear sign that the field has come of age. The field has indeed reached a turning point, Feringa comments in Nature: Now the field has reached a turning point. “We've made 50 or 60 different motors,” he says. “I'm less interested in making another motor than actually using it.”
Nature News Feature: The tiniest Lego : a tale of nanoscale motors, rotors, switches and pumps.
More news
-
19 December 2025
Mariano Méndez receives Argentine RAÍCES award
-
18 December 2025
Why innovate, and for whom?
-
17 December 2025
Ben Feringa wins Feynman Prize
