Electromagnetic radiation
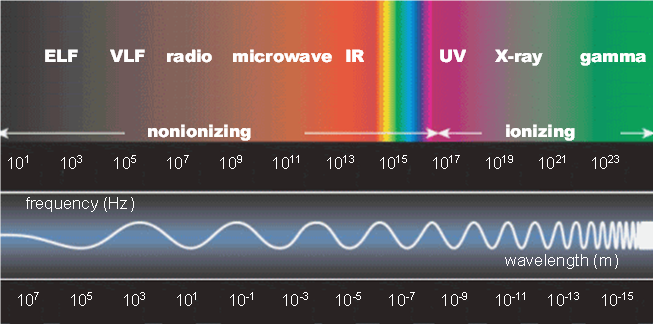

Electromagnetic radiation is the propagation of electrical and magnetic waves through space. Radio waves, light, X-rays and γ-radiation are all forms of this radiation. The waves are described by a wavelength (λ) and a frequency (ν), the product of which is equal to the speed of light. The speed of light in vacuum is fixed to be equal to 299,792,458 m/s.
wavelength (λ) × frequency (ν) = speed of light (c)
Electromagnetic radiation can also be understood as a stream of photons (light particles).
History
The Scottish mathematician and physicist James Clerk Maxwell (1831 – 1879) has formulated the basic equations on which the entire classical electromagnetic theory is built.
Related concepts
| Last modified: | 11 April 2024 3.27 p.m. |
View this page in: Nederlands
